What is Economics?

Economics allocates the limited resources for our unlimited wants.
Economics have been defined by many people and many websites.
Common definitions are:
David N.Hyman defined economics as a study of how scarce resources are allocated among alternative uses.
L.Robbins defined economics is a science that studies human behavior as relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.
K.E Case defined economics is a study of how people use their limited resources to try to fulfil unlimited wants and involve alternatives or choices.
Economics have been defined by many people and many websites.
Common definitions are:
David N.Hyman defined economics as a study of how scarce resources are allocated among alternative uses.
L.Robbins defined economics is a science that studies human behavior as relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.
K.E Case defined economics is a study of how people use their limited resources to try to fulfil unlimited wants and involve alternatives or choices.
Four Factors of Production
- What to produce?
Every nation has to take important decision of what to produce because of the limited economic resources. - How To Produce?
In every production they have find the cheapest methods of production. They are alternative techniques of producing good and services. - For Whom To Produce?
Distribution of income, how the national income distributed. - Entrepreneur - Human ability to combine the other three factors ( capital, land, labour ) to develop production of goods and services.
What is Scarcity?
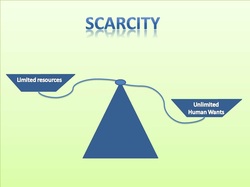
Scarcity is limited resources for unlimited wants, because of scarcity, various economic decisions must be made to allocate resources efficiently. A resource is considered scarce when its availability is not enough to meet its demand.
What is Demand?The demand is the willingness and ability to buy certain amount of goods in certain period of time at particular price when other factors remain same (ceteris paribus).
What is Supply?Supply is the willingness and ability to sell or produce a certain product and services in certain period of time at particular price, ceteris paribus.
|
Demand and Supply Curve |
What are the difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics?
What are the Macroeconomic Goals?
- Full Employment, it is almost impossible to get full employment, because they are always some people who are not happy with their current job and searching for new jobs or students who have just graduated and looking new jobs. Full employment is when unemployment rate is equal to all types of unemployment except cyclical unemployment.
Another meaning of full employment is when the economy is using all the available resources more efficiently to attain maximum output. - Price Stability, the goal of the economy is to keep the inflation rate as low as possible to maintain price stability. High inflation rate will reduce the purchasing power due to increase in prices.
- Economic Growth, to achieve economic growth the country must be operating at maximum capacity to increase the production of output. Economic grow can be measured by evaluating the full production of output per capital.
- Equitable distribution of Income, to achieve this goal most of the nations try to narrow the gap between the lower income and higher income groups of people. Governments will impose higher income tax to high income groups and lower income tax to lower income groups to narrow the gaps.
What is National Income?
National Income can defined as, the total money value of all goods and services produced by a country and deducting the depreciation value of the machines used in production during one year.
What are the concepts of National Income?
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP), is the total value of the all final goods and services produced within a country during one year period. The formula to calculate GDP is:
GDP at market price = C+I+G+(X-M)
GDP at factor cost = GDP at market price - indirect taxes + subsidies
C = Personal Consumption
I = Investment
G = Government Spending
X = Export
M = Import - Gross National Product (GNP), is the total market value of all final goods and services produced by the citizens of a national during one year even if the citizens are in different country.